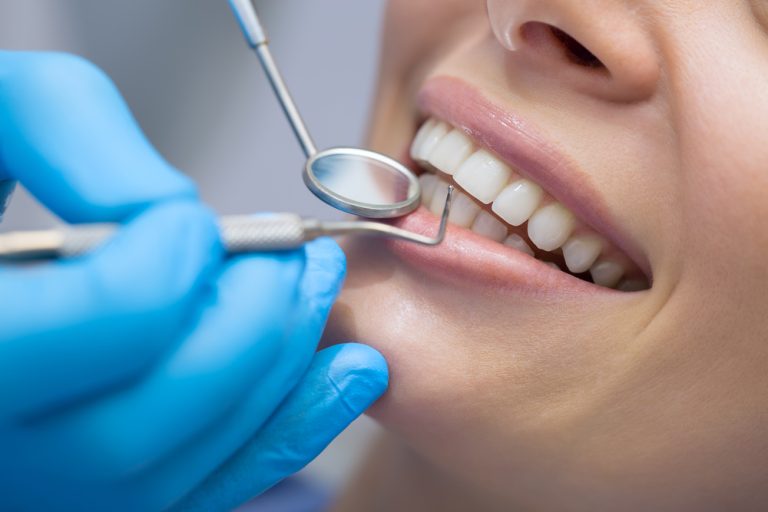
Critical periods for guaranteeing good oral health are pregnancy and early childhood. Children between toddler age and 3rd grade in New York are the ones who are at most risk of tooth decay. Statistics revealed that 60% of children in low-income and 48% in high-income families suffered from tooth decay.
There is a great New York, NY health & wellness center that is trying to reduce the rampancy of dental caries disease in the city. It is scary that our children continue to agonize from unaddressed tooth decay. Overall improvements in oral health have to be done if there is going to be a significant decrease in dental caries.
Children are suffering. Disparities are also apparent concerning ethnicity, race, and poverty. Those at most risk are the institutionalized, chronically ill, the older people, the poor, and minorities.
Effects of Untreated Dental Caries
Toothache or discomfort with associated untreated dental caries causes impaired cognitive development and weight gain. Serious dental decay contributes to the failure to thrive (FTT). Dental caries makes eating painful, thus decreasing the intake of foods.

Pain caused by prevailing caries makes sleeping difficult. Disturbed sleeping habits can affect growth and glucosteroid production. Untreated dental caries affects the children’s dietary intake and overall quality of life.
The aftermath of soaring caries levels include diminished learning abilities, school absence, emergency dental visits, and hospitalizations. Dental pain affects the economy since it makes parents take time off to take their children to the hospital.
Chronic inflammation is another possible mechanism of how pulpitis with untreated dental caries affects development. Chronic dental abscesses and pulpitis (chronic inflammation) affect metabolic pathways – whereby erythropoiesis is affected by cytokines. For instance, interleukin-1 (IL-1), which contains a wide range of inflammation actions, can induce erythropoiesis inhibition.
Hemoglobin suppression leads to anemia as a result of the bone marrow’s inhibition to produce erythrocyte. The longer dental caries remain untreated, the more costly and extensive they become. In New York, the approximate treatment cost of severe early dental caries is $4,500 per child.
Two varnish applications containing fluoride elements cost approximately $60 per child. A noninvasive and preventive sealant application goes for $43 per tooth, rising to $55, depending on the level of deterioration. This is because the tooth might need restorative treatment by being refilled.
If a tooth is left to decay further, it can cost $493 for a crown, and $406 for a root canal. These sums are significant, and there are many families out there who struggle to make ends meet. That is why preschool children should be monitored at all times and be prevented from eating sugary items.
Dental treatment contributes positively to the social and psychological aspects of a child’s life. These improvements include better eating and sleeping habits and less pain. One study revealed that parents whose children had been treated showed signs of increased social interaction.
Prevention is always better than cure. Early treatment of dental caries increases growth rates significantly. What’s worrying is the high numbers of untreated caries in New York, which indicate that more work has to be done!