Month: June 2024
Complications of Diabetic wounds
More than 30 million people in the United States have diabetes. There are different types of diabetes, including type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and […]
High-quality ingredients are provided to deliver a great customer experience
The customers can ensure to make an informed decision about the CBD products by understanding the benefits and advantages. If you are ready to purchase […]
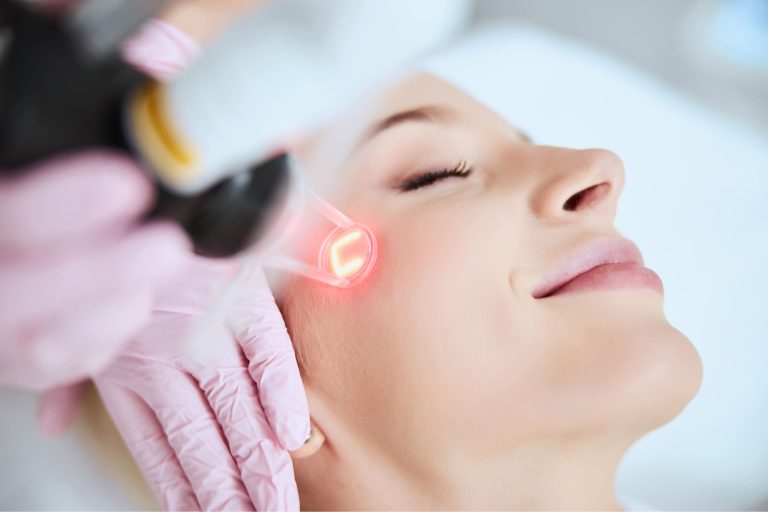
Pre-Laser Hair Removal Preparations You Should Know And What To Expect
Nobody wants to deal with unwanted hair. That is why if you have considered laser hair removal treatments, then you need to know how you […]
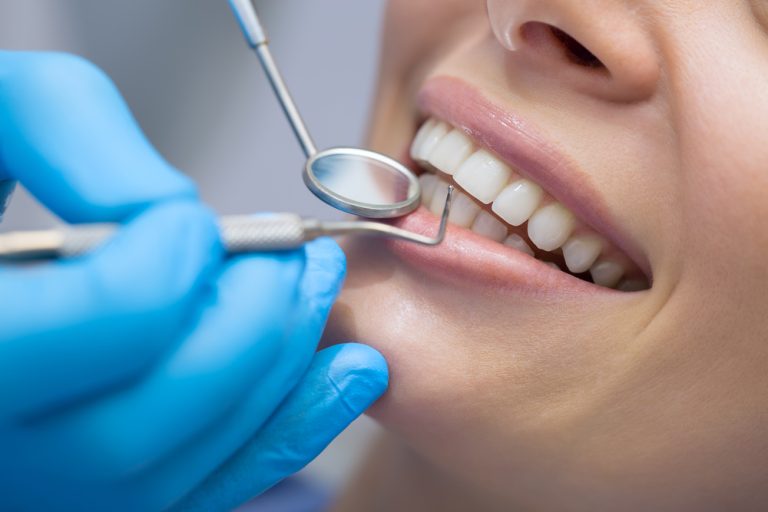
When do you need bone grafting before dental implants?
A Dental implant is an artificial tooth that is implanted into the jawbone. It is used when adults lose one or some of their teeth and […]
How to Care for Your Teeth during Holidays?
We all have routines that we follow consciously or unconsciously, and they greatly influence our lifestyles. Most people have a dental care routine that helps […]
Hiring a Family Dentist
If you have moved to a new place, looking for a new dentist is one of the main things you have to look into. It […]
The Eye Lab In Melbourne Best For Optometric Services
The eye lab which is located in Melbourne is one of the most reputed optical eye check-up clinics along with sunglasses store with large collection […]
The hair thinning problem is a big issue
As we all know that hair loss is a major problem now a day’s. Start from the teenage to elderly aged people, most of us […]
Hair transplantation is the permanent hair fall remedy clinically
In today’s busy schedule world, the most common problem incurred to both men and women is hair damage. Either the hair gets dry or it […]
Want to treat obesity? Cetilistat will help you
Everyone is now too conscious about health and there is nothing wrong with it. Health must be the top priority of every being. With increasing […]